Solid Injection Molding and Extrusion Molding are both crucial processes in the manufacturing of rubber and silicone products. They each have their unique characteristics and are suitable for different types of products. Understanding the differences between these two molding techniques is essential for manufacturers to make informed decisions about which process is best suited for their specific production needs.
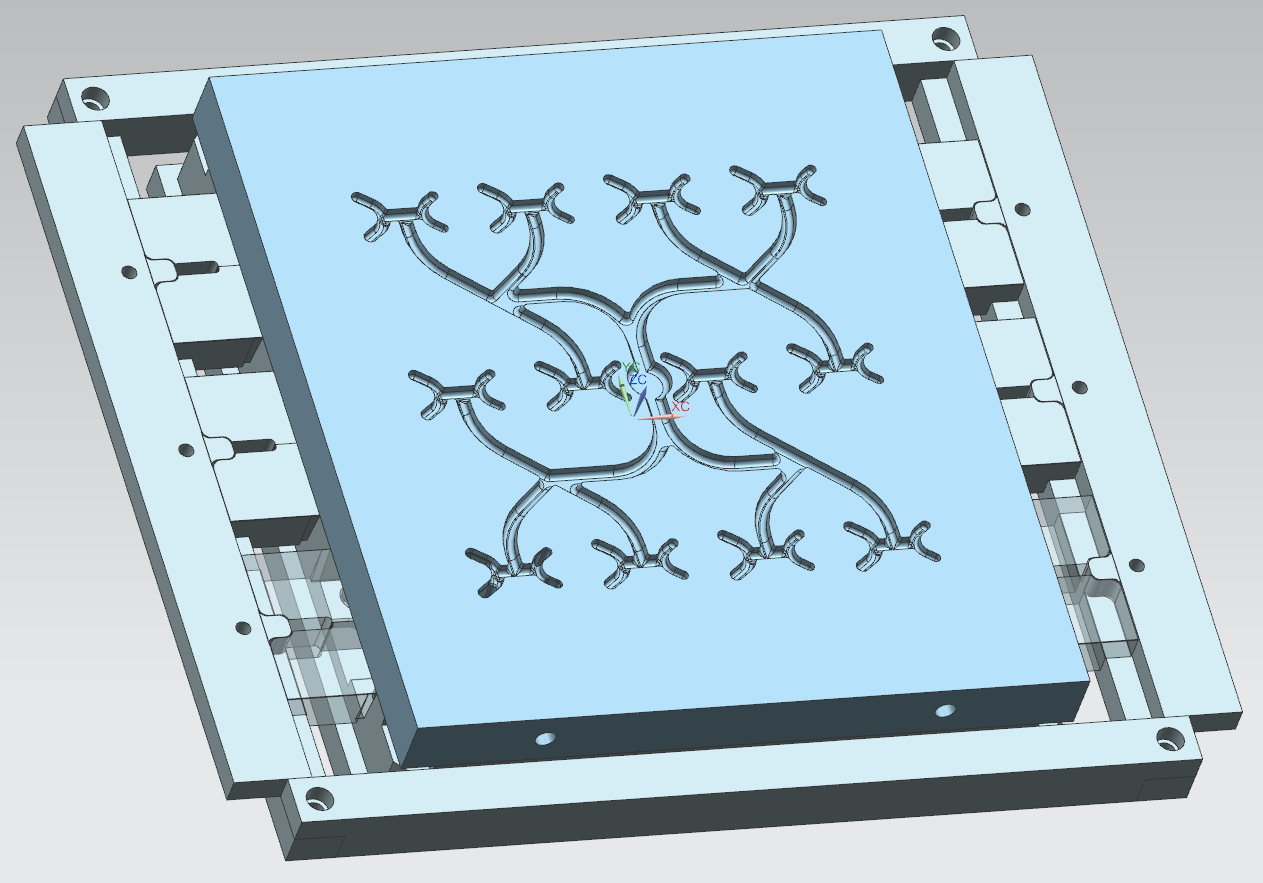
Solid injection molding is ideal for producing small to medium-sized rubber and silicone products with intricate details and complex shapes. This process is well-suited for items such as O-rings, grommets, and precision parts that require specific designs and features. The use of a solid mold allows for precise control over the shape and details of the final product, making solid injection molding the preferred choice for products with high dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances.
Extrusion molding, on the other hand, is best suited for producing rubber and silicone products with a constant cross-section, such as tubing, seals, gaskets, and profiles. The continuous nature of the extrusion process allows for high production speeds and cost-efficiency, making it ideal for large-scale production runs of products with uniform shapes and sizes. Extrusion molding is also versatile and can produce products of varying lengths, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
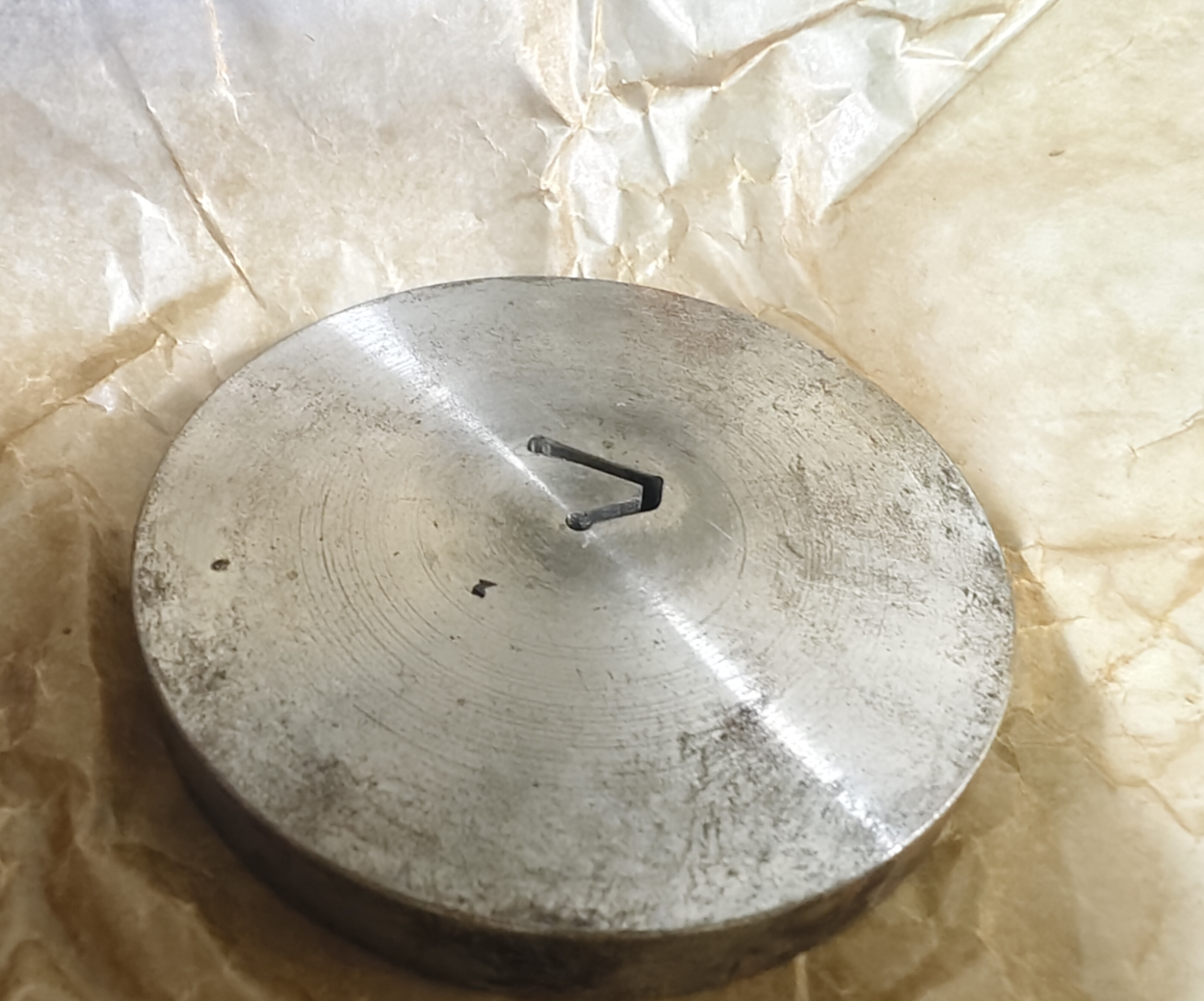

When it comes to tooling and equipment, solid injection molding relies on solid molds made of metal or other durable materials. These molds are typically designed to create a single product at a time, which can result in longer production times and higher tooling costs, especially for complex parts. Conversely, extrusion molding uses an extruder and a die to continuously shape the material, resulting in lower tooling costs and faster production speeds, particularly for products with a constant cross-section.
In terms of production speed and cost, solid injection molding tends to be slower and more labor-intensive, especially for smaller production runs. Each part is produced individually in a mold, which can result in higher production costs per unit. Extrusion molding, on the other hand, offers higher production speeds and lower production costs, particularly for larger production runs, making it a cost-effective option for high-volume manufacturing.
In conclusion, both solid injection molding and extrusion molding are valuable techniques for shaping rubber and silicone materials into a wide range of products. Solid injection molding is best suited for intricate and complex parts, while extrusion molding is ideal for producing products with a constant cross-section and is more cost-effective for larger production runs. By understanding the differences between these two molding techniques, manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize their production processes and meet the specific requirements of their products.
Your kind inquiry is highly appreciated Oliver.Liu@bello-rubber.com.